📲 Digital Ration Revolution: CBDC-based PDS
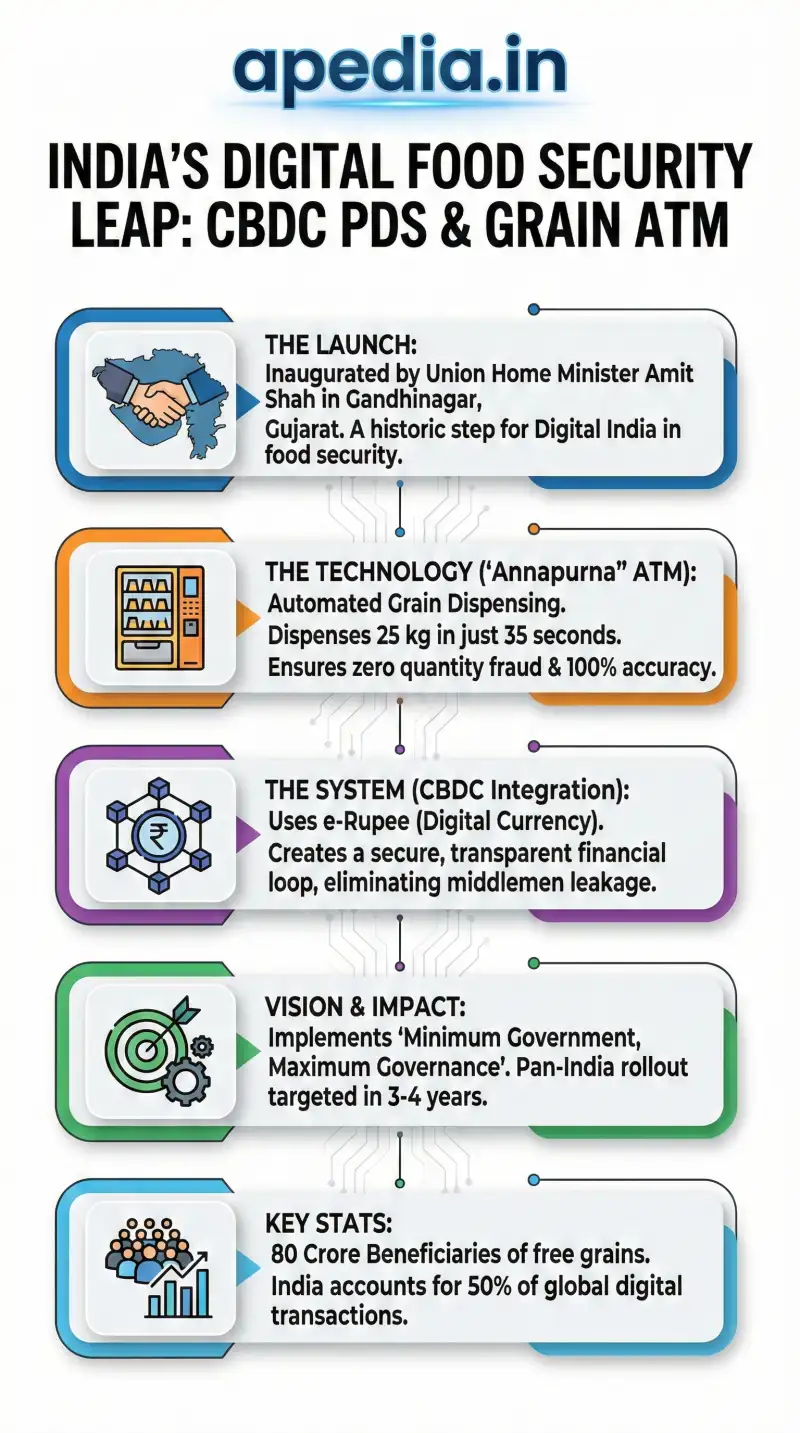
In a historic step towards ensuring 100% transparency in food security, Union Home Minister Shri Amit Shah has launched India's first Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC)-based Public Distribution System (PDS) in Gandhinagar, Gujarat. This initiative marks the entry of Digital India into the granular level of food grain distribution.
25 Kg
Dispensed in 35 Sec
3-4 Yrs
Pan-India Rollout
80 Cr
Beneficiaries
⚙️ Key Mechanisms & Innovations
The new system operationalizes Prime Minister Modi’s vision of "Minimum Government, Maximum Governance" by removing human intervention and corruption from ration delivery.
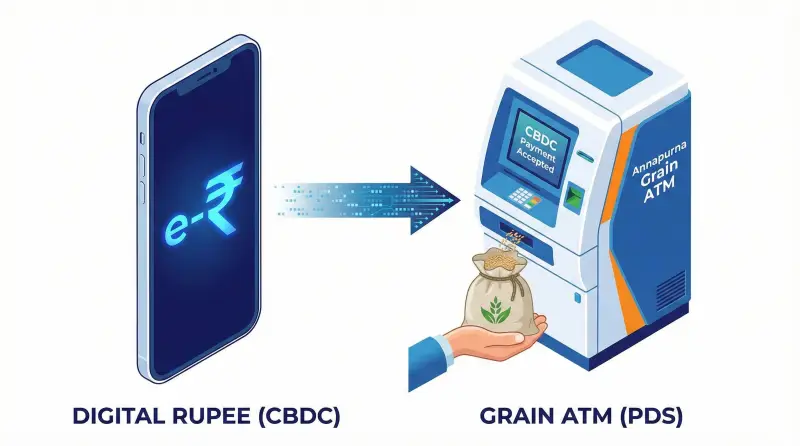
🏧 The 'Annapurna' ATM
A Grain ATM launched alongside the system that ensures accurate quantity and quality, dispensing 25 kg of grains in just 35 seconds, eliminating weighing fraud.
💱 CBDC Integration
Utilizes the e-Rupee (Digital Currency) to ensure that the financial subsidy loop is secure, transparent, and leaves no room for middlemen.
🛡️ Farmer Safeguards
The government emphasized that recent FTAs (Free Trade Agreements) with the EU, UK, and USA have been designed to strictly protect the interests of Indian farmers and the dairy sector.
📊 Comparative Progress: Then vs. Now
The launch highlighted significant shifts in agricultural policy and digital inclusion over the last decade.
- 🌾 Agriculture Budget: Increased from ₹26,000 Crore (Previous Govt) to ₹1.29 Lakh Crore (Current Govt).
- 🚜 Trade Policy: Contrast drawn between the Dunkel Proposal (which allegedly made farmers insecure) and current FTAs which open global markets while protecting local interests.
- 💻 Digital Inclusion: India now accounts for 50% of the world's digital transactions, a leap from when 60 crore citizens lacked bank accounts.
📚 UPSC Corner: Prelims Quiz
1. The CBDC-based Public Distribution System (PDS) was recently launched in which city?
Answer: B
2. What is the primary function of the 'Annapurna' machine mentioned in the launch?
Answer: B
📝 Mains Practice Questions & Model Answers
Q1. "Technology is the antidote to corruption in welfare delivery." Discuss how the integration of CBDC and Grain ATMs can reform the Public Distribution System (PDS) in India. (GS-3: Economy/PDS) - 250 Words
Model Answer Synopsis
Introduction
The launch of CBDC-based PDS and 'Annapurna' Grain ATMs marks a shift from a leak-prone, manual system to a digitized, automated welfare infrastructure, aiming to implement "Minimum Government, Maximum Governance."
Addressing Structural Flaws
1. Quantity Fraud: Grain ATMs (25kg/35sec) eliminate manual weighing errors and "short-changing" by ration dealers.
2. Financial Leakage: CBDC (e-Rupee) ensures that subsidies travel digitally from the treasury to the beneficiary without diversion by middlemen.
2. Financial Leakage: CBDC (e-Rupee) ensures that subsidies travel digitally from the treasury to the beneficiary without diversion by middlemen.
Broader Impact
It ensures the "Right to Food" is honored with dignity (no standing in long queues) and transparency. It complements schemes like PM SVANidhi and DBT, creating a holistic digital welfare ecosystem.
Conclusion
While infrastructure rollout (Pan-India in 3-4 years) is a challenge, this tech-stack is essential to sustain the massive burden of providing free grains to 80 crore citizens efficiently.
Source Information: PIB Release ID: 2228387 (Feb 15, 2026)
Ministry of Home Affairs
Ministry of Home Affairs