🌱 NBA Realizes ₹2.40 Cr for Biodiversity
The National Biodiversity Authority (NBA), functioning under the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change, has achieved a significant milestone by collecting ₹2.40 crore in just 45 days under the Access and Benefit-Sharing (ABS) framework. This underscores the potential of India's bio-resources in driving a sustainable economy.
₹266 Cr
Cumulative Total
₹83 Cr
Seed Sector Contribution
45 Days
Timeframe
⚖️ The ABS Framework Explained
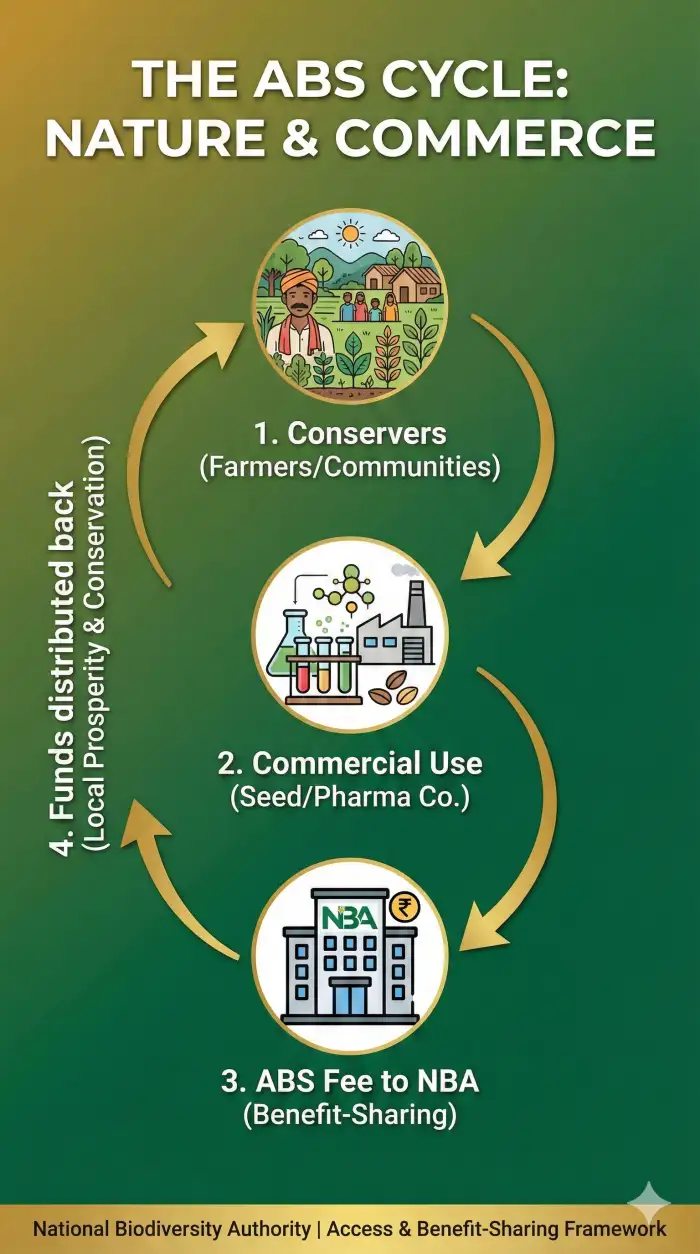
The ABS mechanism ensures that when companies use India's biological resources for commercial purposes, a fair share of the benefits is returned to the conservers of these resources.
Source Resources
Funds were realized from the use of bio-resources like Rice, Mustard, Cotton, Tomato, and Seaweed for developing hybrid seeds.
Key Contributors
Major contributions came from M/s Pioneer Overseas Corporation (₹2.30 Cr), followed by other seed companies like East West Seeds and Advanta.
Beneficiaries
The amount is shared with farmers, local communities, and Biodiversity Management Committees (BMCs) who conserve these resources.
Global Targets
This aligns with the Kunming–Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework (Target 13) and the Nagoya Protocol.
📚 UPSC Corner: Prelims Quiz
1. The National Biodiversity Authority (NBA) was established under which Act?
Answer: C
2. Which international protocol specifically deals with Access and Benefit-Sharing (ABS)?
Answer: C
3. According to the recent report, which sector is the second-largest contributor to ABS funds after Red Sanders?
Answer: B
4. Biodiversity Management Committees (BMCs) are constituted at which level?
Answer: C
5. Which global biodiversity framework's Target-13 emphasizes ABS measures?
Answer: B
📝 Mains Practice Questions & Model Answers
Q1. "The Access and Benefit-Sharing (ABS) mechanism is a vital tool for ensuring that the commercial use of biodiversity translates into local prosperity." Discuss the significance of ABS in the context of the Biological Diversity Act, 2002. (GS-3: Environment) - 250 Words
Model Answer Synopsis
Introduction
The Biological Diversity Act, 2002 was enacted to fulfill India's obligations under the Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD). Its third objective, 'Fair and Equitable Sharing of Benefits', is operationalized through the ABS framework.
Significance of ABS
1. Economic Justice: It prevents 'Biopiracy' by ensuring that companies using Indian biological resources (like Red Sanders or medicinal plants) share a percentage of their profits with the NBA/State Biodiversity Boards.
2. Incentivizing Conservation: The funds collected (over ₹266 Cr so far) are ploughed back to local Biodiversity Management Committees (BMCs) and conservers, incentivizing them to protect their ecosystem.
3. Sovereign Rights: It reaffirms India's sovereign right over its biological resources against foreign exploitation (as seen in the Pioneer Overseas case).
2. Incentivizing Conservation: The funds collected (over ₹266 Cr so far) are ploughed back to local Biodiversity Management Committees (BMCs) and conservers, incentivizing them to protect their ecosystem.
3. Sovereign Rights: It reaffirms India's sovereign right over its biological resources against foreign exploitation (as seen in the Pioneer Overseas case).
Conclusion
ABS bridges the gap between commerce and conservation. Effective implementation ensures that the custodians of biodiversity (tribals, farmers) are not left behind in the bio-economy boom.
Q2. Evaluate the role of the National Biodiversity Authority (NBA) in implementing the Nagoya Protocol in India. What challenges does it face? (GS-3: Environment) - 150 Words
Model Answer Synopsis
Role of NBA
As the competent national authority, the NBA regulates access to biological resources. It processes applications for intellectual property rights (IPR) and transfer of research results, ensuring compliance with the Nagoya Protocol's ABS provisions.
Challenges
1. Compliance: Many industries (Ayush, Cosmetics) are often unaware or reluctant to pay ABS, viewing it as an additional tax.
2. Identification: Tracing the exact origin of bio-resources in complex supply chains is difficult.
3. Distribution: Ensuring the money actually reaches the grass-root level BMCs and benefits the specific community remains a logistical challenge.
2. Identification: Tracing the exact origin of bio-resources in complex supply chains is difficult.
3. Distribution: Ensuring the money actually reaches the grass-root level BMCs and benefits the specific community remains a logistical challenge.
Source Information: PIB Release ID: 2227366 (Feb 13, 2026)
Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change
Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change