🌾 Saving Mother Earth: Farmers Lead the Way
In a landmark initiative, the Department of Fertilizers convened a high-level dialogue with eight Padma Awardee progressive farmers to formulate a national strategy for balanced fertilizer use. This aligns with PM Narendra Modi’s vision of “Save Mother Earth (धरती मां को बचाओ)”.
8
Padma Farmers
Zero
Poison Farming
Policy
From Grassroots
🚜 Wisdom from the Field (Key Suggestions)
The brainstorming session translated grassroots experience into actionable policy inputs to curb the deterioration of soil health.
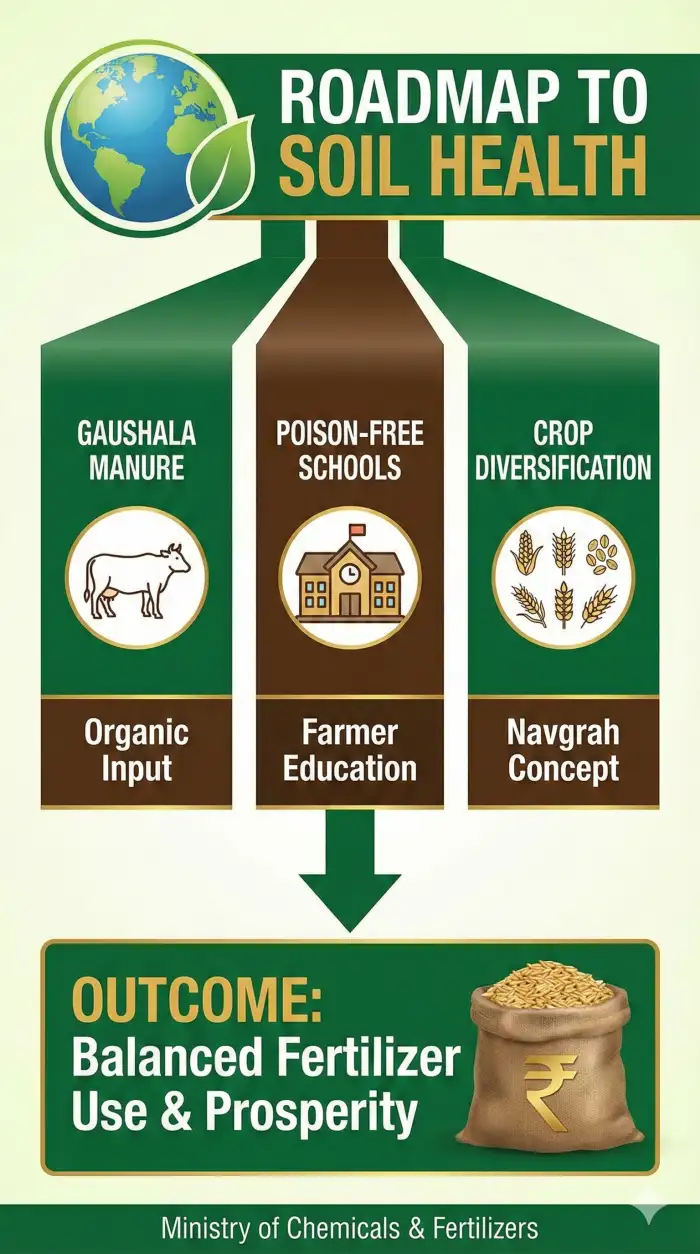
Poison-Free Schools
Shri Umashankar Pandey proposed launching "Poison-Free Farming Schools" to educate farmers on sustainable practices and move away from chemical dependency.
Crop Rotation
Shri Ram Sharan Verma emphasized crop diversification and debunked the myth that "more fertilizer means more profit," advocating for rationalized bag sizes.
Gaushala Integration
Shri Kanwal Singh suggested turning Gaushalas into organic manure production units to create a structured chain for natural farming.
Navgrah Rituals
Shri Nek Ram Sharma noted that traditional rituals using nine grains symbolize crop diversity, crucial for soil health and forest conservation.
📚 UPSC Corner: Prelims Quiz
1. The "Save Mother Earth" campaign mentioned in the release is primarily associated with which objective?
Answer: B
2. Which Department organized the session with Padma Awardee farmers?
Answer: B
3. Who is the Union Minister for Chemicals and Fertilizers mentioned in the release?
Answer: B
4. What major suggestion was made regarding 'Gaushalas' during the session?
Answer: B
5. The concept of "Poison-Free Farming School" was proposed by which Padma Awardee?
Answer: B
6. The "Navgrah" rituals mentioned by Shri Nek Ram Sharma symbolize:
Answer: B
7. To ensure balanced fertilizer use, participants suggested establishing fertilizer plants at which administrative level?
Answer: C
8. What is the primary reason cited for the deterioration of soil health?
Answer: B
9. Which initiative was suggested to be led by FPOs (Farmer Producer Organizations)?
Answer: B
10. The meeting emphasized shifting the farmer mindset from "More fertilizer means more profit" to:
Answer: B
📝 Mains Practice Questions & Model Answers
Q1. "Imbalanced use of fertilizers has degraded soil health, threatening food security in the long run." Discuss. How can the integration of traditional knowledge (as suggested by Padma Awardee farmers) and modern policy interventions address this crisis? (GS-3: Agriculture) - 250 Words
Model Answer Synopsis
Introduction
The Green Revolution ensured food security but at the cost of soil health due to the excessive use of Urea and DAP. The NPK ratio in many states is skewed far beyond the ideal 4:2:1.
The Crisis
1. Soil Degradation: Loss of organic carbon, micronutrient deficiency (Zinc, Boron), and groundwater contamination.
2. Economic Burden: Rising subsidy bill for the government and increased input cost for farmers without proportional yield increase.
2. Economic Burden: Rising subsidy bill for the government and increased input cost for farmers without proportional yield increase.
Solutions (Traditional + Modern)
1. Gaushala-based Organic Farming: As suggested by Shri Kanwal Singh, integrating livestock creates a closed-loop system for organic manure, reducing chemical dependency.
2. Crop Diversification: Shri Nek Ram Sharma’s "Navgrah" concept promotes multi-cropping, which naturally replenishes soil nutrients.
3. Policy Support: Promoting "Poison-Free Farming Schools" and establishing natural fertilizer plants at the Gram Panchayat level decentralizes production and consumption.
2. Crop Diversification: Shri Nek Ram Sharma’s "Navgrah" concept promotes multi-cropping, which naturally replenishes soil nutrients.
3. Policy Support: Promoting "Poison-Free Farming Schools" and establishing natural fertilizer plants at the Gram Panchayat level decentralizes production and consumption.
Conclusion
A "Jan Andolan" for soil health requires shifting from "Input-Intensive" to "Knowledge-Intensive" agriculture.
Q2. Evaluate the potential of "Natural Farming" and "Organic Manure" in restoring soil vitality. What are the challenges in scaling these practices nationwide? (GS-3: Environment/Agriculture) - 150 Words
Model Answer Synopsis
Potential
Natural farming (Zero Budget Natural Farming) restores soil microbiome and increases water retention. Organic manure (from Gaushalas/Compost) improves soil structure and carbon content, unlike chemical fertilizers which only provide N-P-K.
Challenges in Scaling
1. Yield Dip: Initial transition period often sees a drop in yield, discouraging farmers.
2. Supply Chain: Lack of organized supply for bio-inputs compared to the robust network of chemical fertilizer shops.
3. Mindset: As noted by Shri Ram Sharan Verma, the deep-rooted belief that "more fertilizer = more profit" needs behavioral change through extension services.
2. Supply Chain: Lack of organized supply for bio-inputs compared to the robust network of chemical fertilizer shops.
3. Mindset: As noted by Shri Ram Sharan Verma, the deep-rooted belief that "more fertilizer = more profit" needs behavioral change through extension services.
Source Information: PIB Release ID: 2227702 (Feb 13, 2026)
Ministry of Chemicals and Fertilizers
Ministry of Chemicals and Fertilizers