🧠 Core Concepts: The Building Blocks
Jean Piaget, a Swiss psychologist, is considered the Father of Child Psychology. He was a Radical Constructivist who believed children are "Little Scientists" who actively construct their own understanding of the world through interaction with their environment.
Schema
Mental Structure
4
Universal Stages
Active
Learning Process
⚙️ Cognitive Processes: How Learning Happens
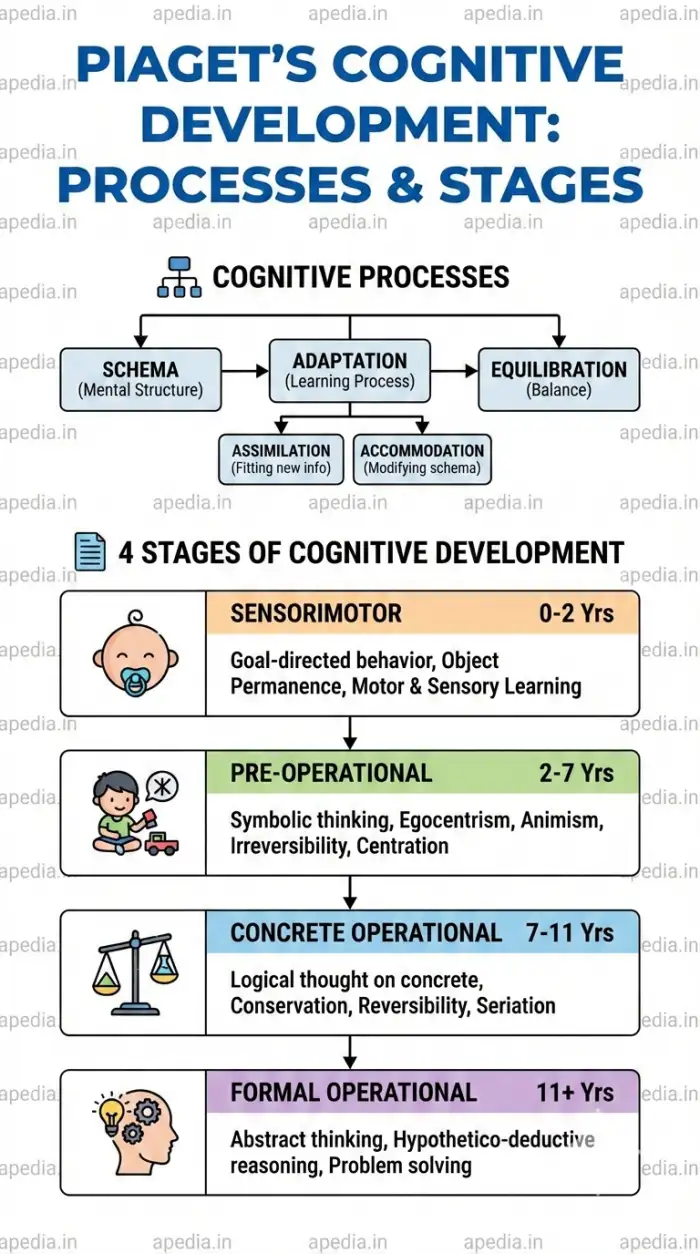
Piaget defined intelligence as the ability to adapt to the environment through specific processes.
📂 Schema
Packets of information or mental models used to organize knowledge (e.g., a mental picture of a 'cat').
🔄 Adaptation
- Assimilation: Fitting new information into an existing schema (e.g., Calling a zebra a "horse").
- Accommodation: Modifying an existing schema to fit new information (e.g., Learning a zebra is striped and different from a horse).
⚖️ Equilibration
The driving force of learning. It is the balance between Assimilation and Accommodation. Confusion causes Disequilibrium, motivating the child to learn.
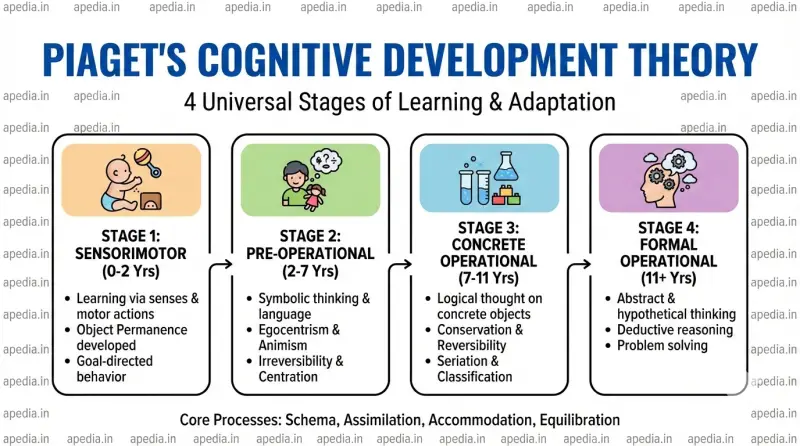
👶 The 4 Stages of Cognitive Development
Piaget proposed that development precedes learning and occurs in four invariant stages.
- 1. Sensorimotor (0–2 yrs): Learning through senses/motor actions. Key feature: Object Permanence (objects exist even when hidden) and Goal-directed behavior.
- 2. Pre-Operational (2–7 yrs): Rise of language. Limitations include Egocentrism (can't take others' view), Animism (toys have feelings), Centration (focus on one aspect), and Irreversibility.
- 3. Concrete Operational (7–11 yrs): Logic begins for concrete things. Key achievements: Conservation (quantity stays same despite shape change), Reversibility, Seriation, and Classification.
- 4. Formal Operational (11+ yrs): Abstract thinking develops. Capable of Hypothetico-Deductive Reasoning (scientific thinking) and problem-solving without physical props.
📚 Quiz Corner
1. In which stage does 'Object Permanence' develop?
Answer: B
2. The inability to understand that 2+3=5 implies 5-3=2 (Reversibility) is a trait of:
Answer: B
Source Information: DSSSB PRT Pedagogy Preparation Series
Link to Study Material
Educational Psychology